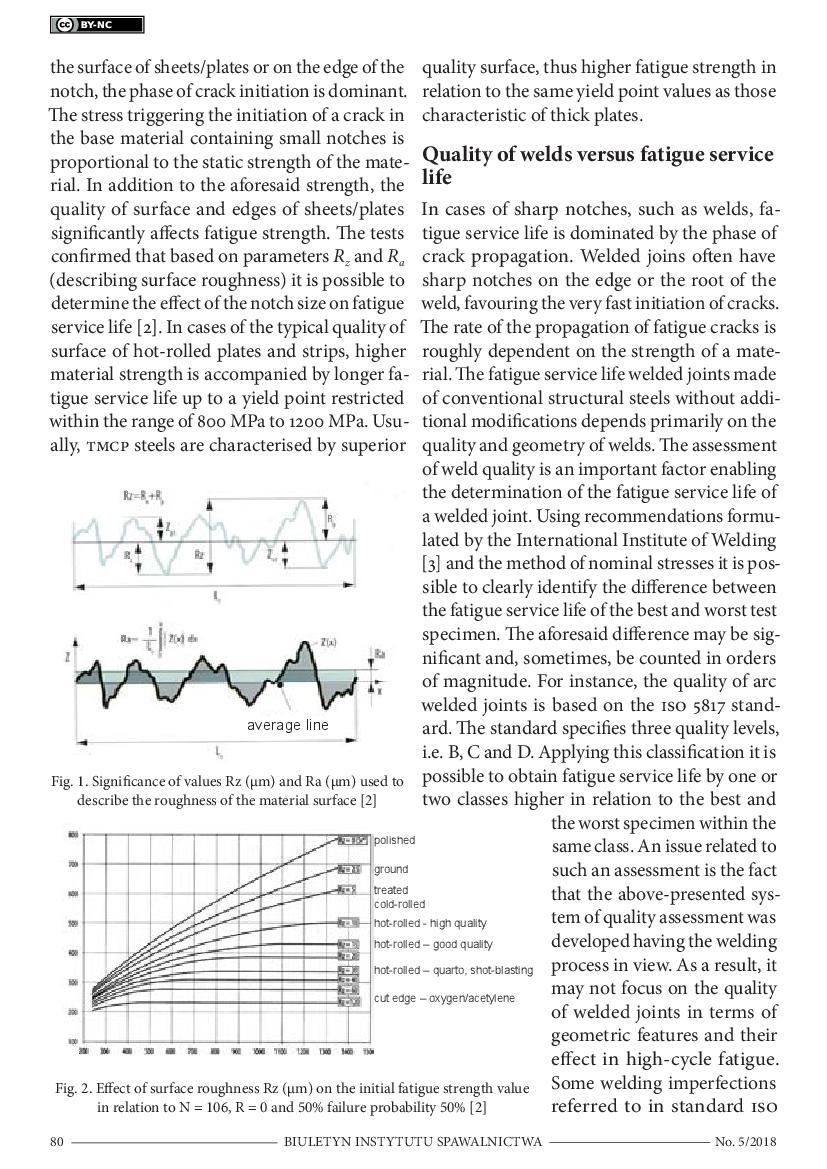
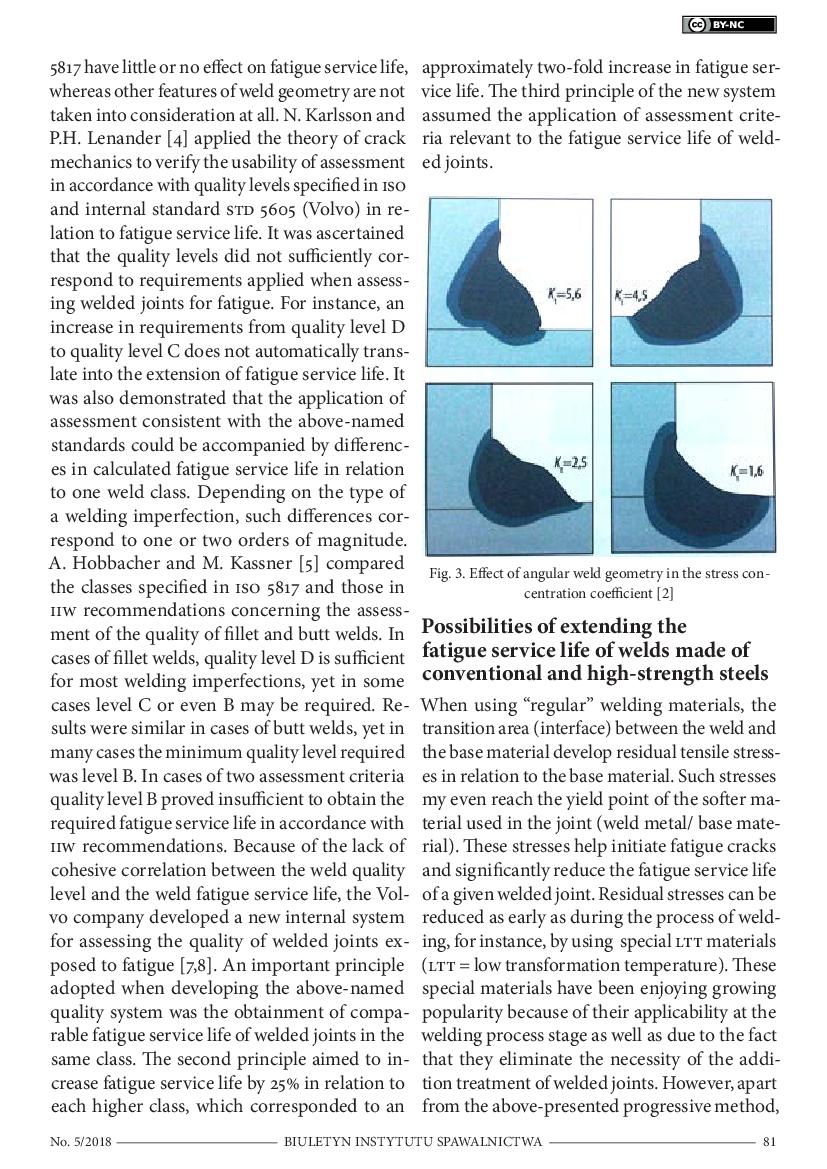
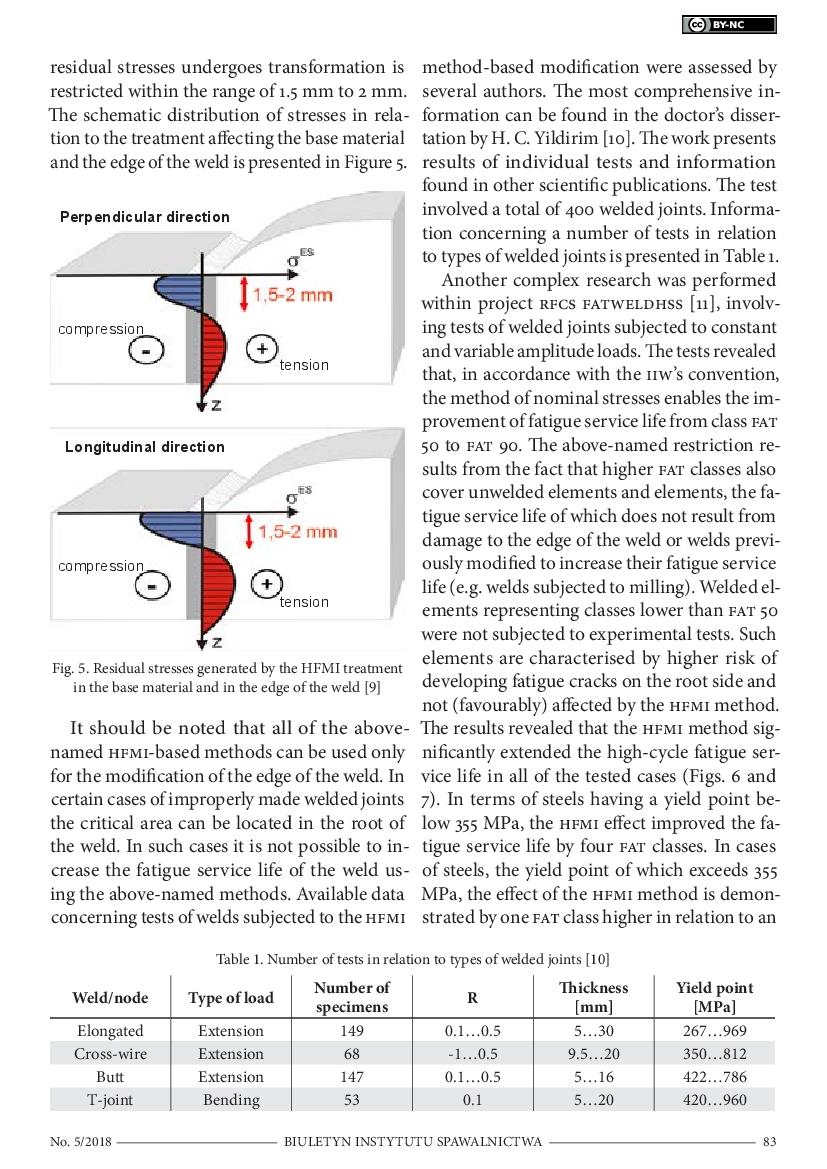
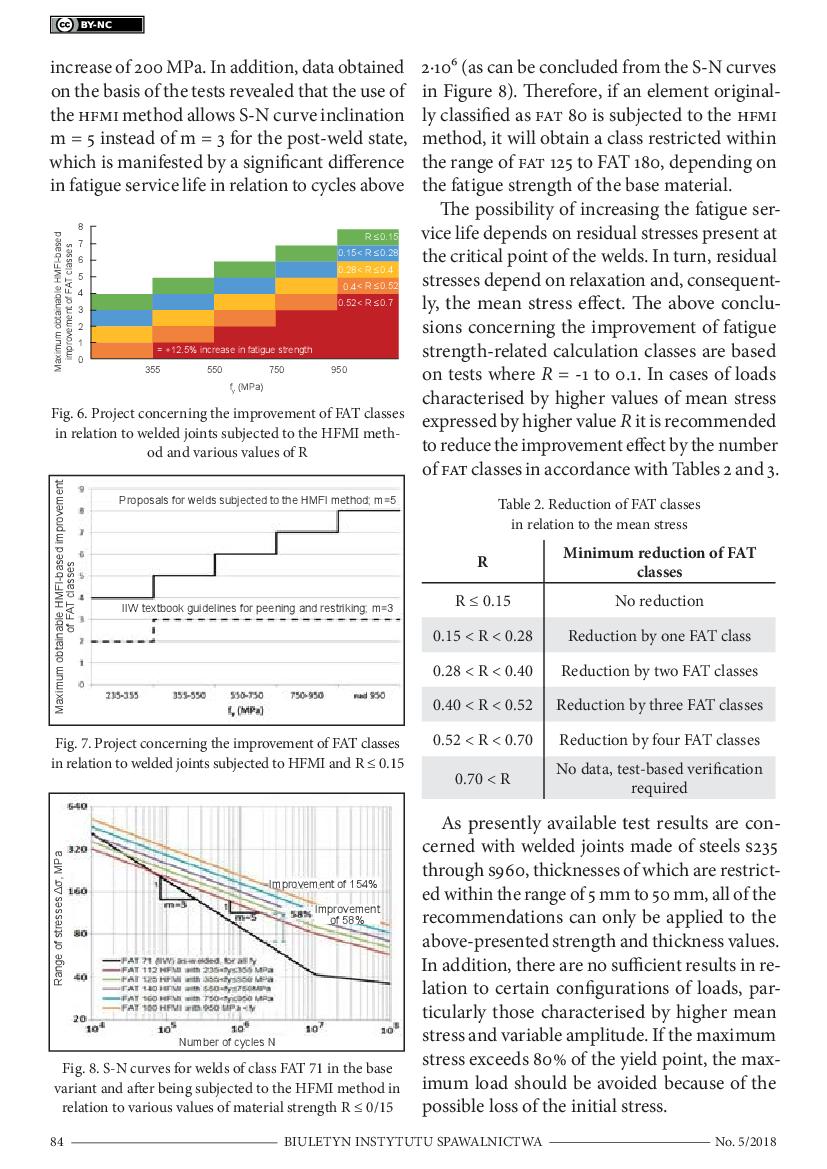
HFMI Method-Based Increase in Fatigue Service Life of Welds in High-Strength Steels
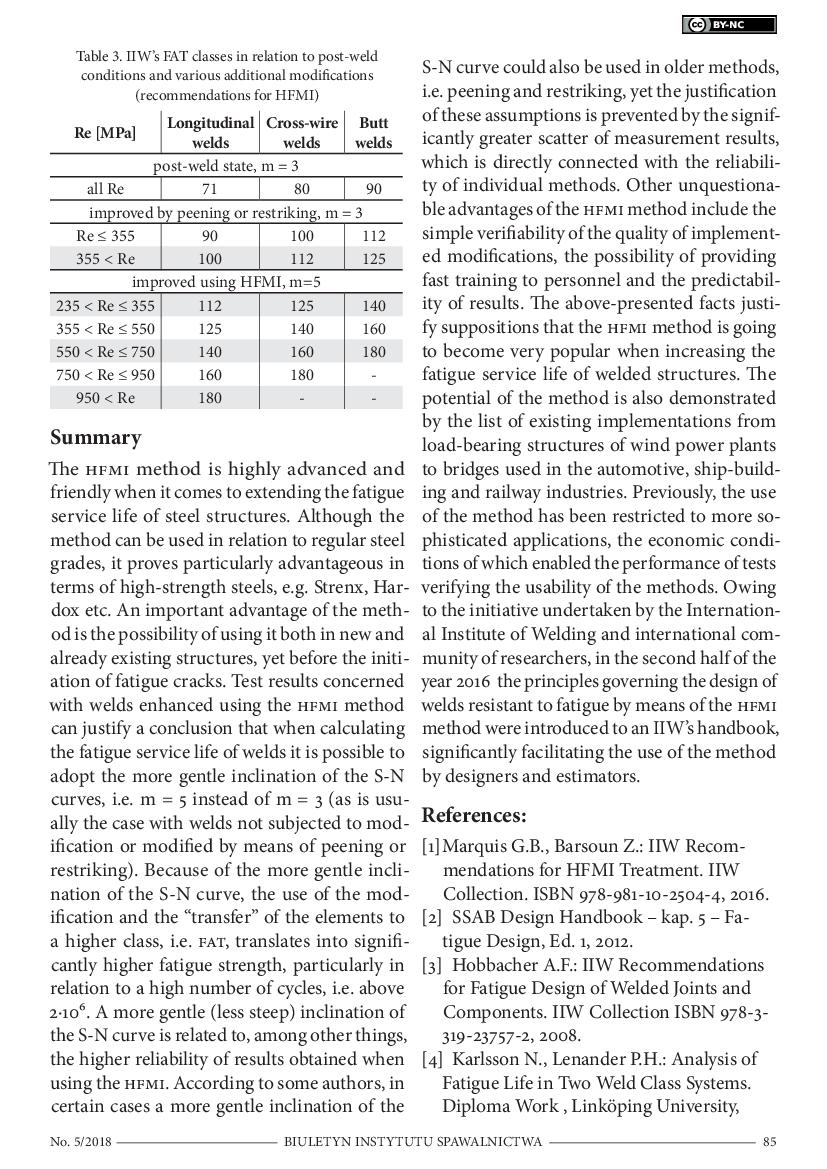
Until recently, the fatigue service life of welded joints exposed to medium and high-cycle fatigue has been a factor restraining the wider use of high-strength steels. Recent research on increasing the fatigue service life of welded joints (weld) has revealed that the aforesaid strength can be significantly increased using the high frequency mechanical impact (HFMI) method. Independently performed tests demonstrated that an increase in fatigue service life was proportional to the strength of the base material subjected to the aforesaid method. The HMFI method involves the application of compressive stress at the critical point of the interface between the weld and the base material. The method is an advanced variant of methods developed in the Soviet Union in the 1970s, used to increase the fatigue service life of welded joints in submarine structures. The method can be applied both in relation to butt and fillet welds. The article summarizes the current state of the art concerning the practical usability of the HFMI method in relation to conventional steels (characterised by lower mechanical properties) and high-strength steels. An important factor affecting increasingly high popularity of the HMFI method is that fact that the method has been included in IIW’s recommendations concerning fatigue-related structural calculations.
doi: 10.17729/ebis.2018.5/8
 1 / 8
1 / 8
 2 & 3 / 8
2 & 3 / 8
 4 & 5 / 8
4 & 5 / 8
 6 & 7 / 8
6 & 7 / 8 8 / 8
8 / 8