Mechanical Properties of Joints Made in Steel S1300QL Using Various Welding Methods
The article presents applications of high-strength quenched steels in
various industrial sectors and the chronological development of various grades
of the aforesaid steels. The research-related tests involved flat butt joints made
in 7 mm thick steel grade S1300QL, welded using the following methods: TIG,
A-TIG, MAG involving the use of a hard flux-cored surfacing wire, MAG method
involving the use of a solid wire, T.I.M.E. method involving the use of a solid
wire, laser welding method without the use of the filler metal, hybrid (HLAW)
method involving the use of a metallic flux-cored wire, electron beam welding
without using the filler metal. The research also involved the performance of the
mechanical properties of the welded joints made in quenched steel S1300QL using
various welding methods. The joints made using the laser welding method,
hybrid welding method and the electron beam welding method were characterised
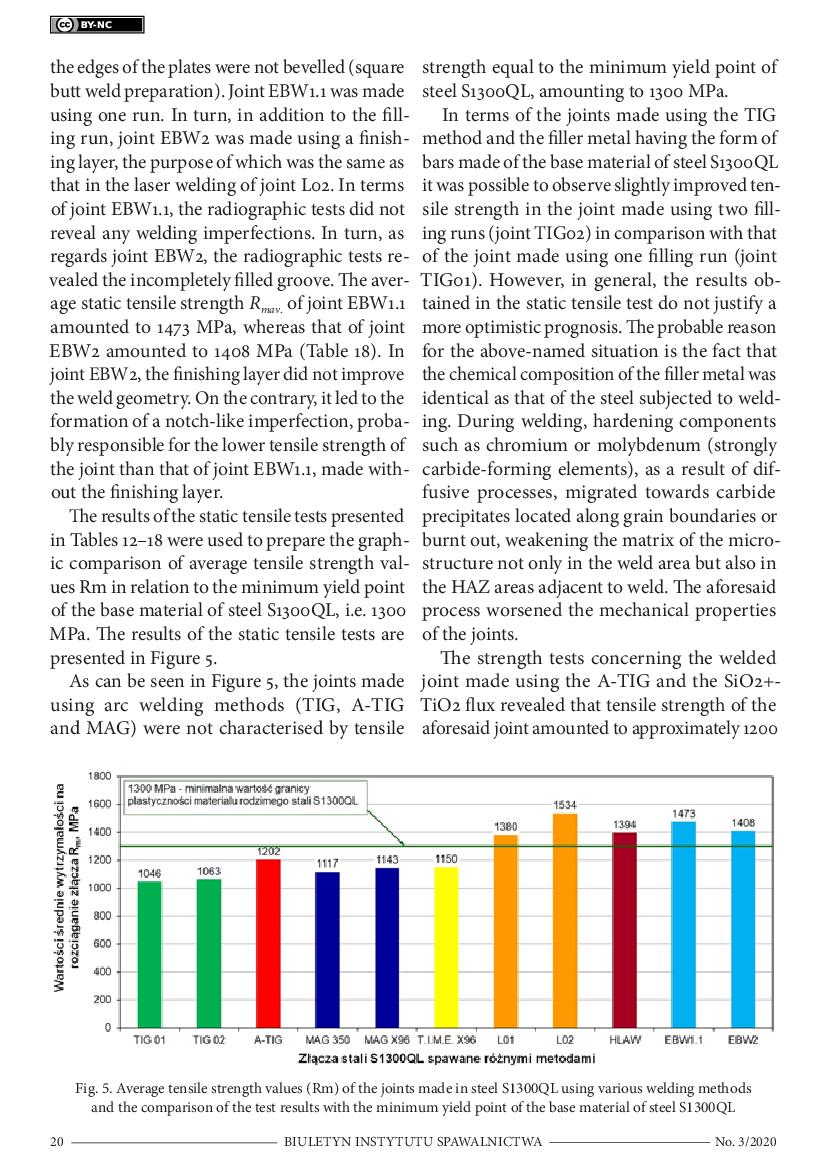
by tensile strength higher than the minimum yield point of steel S1300QL,
amounting to 1300 MPa. In turn, the tensile strength of the joints made in steel
S1300QL using arc welding methods was lower than the minimum yield point
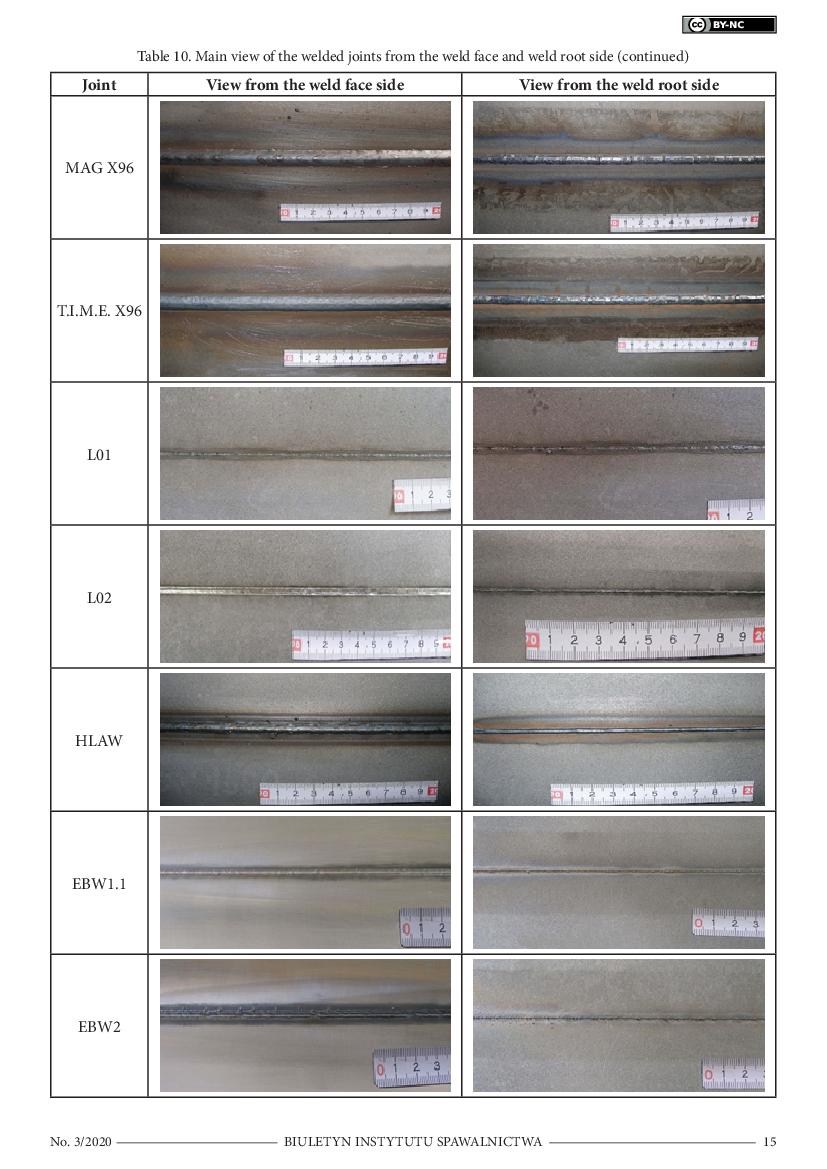
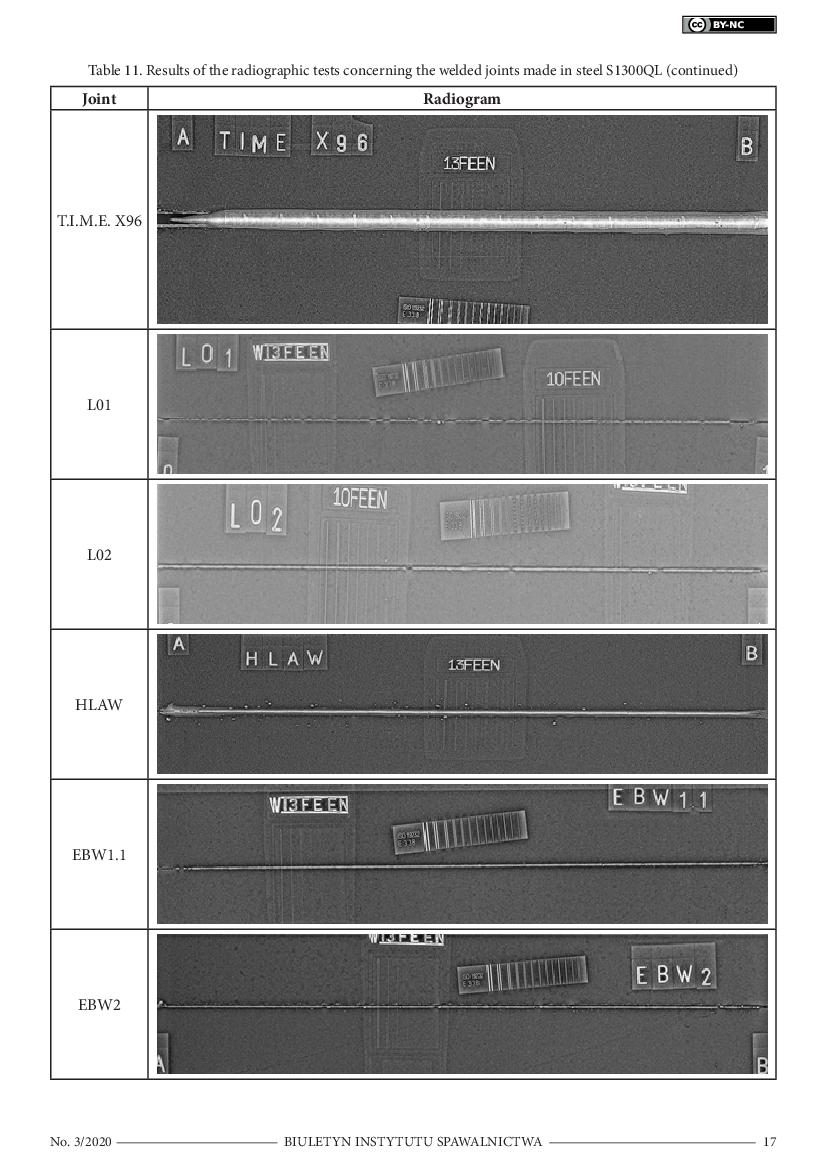
of the steel. All of the test joints were subjected to non-destructive digital radiographic
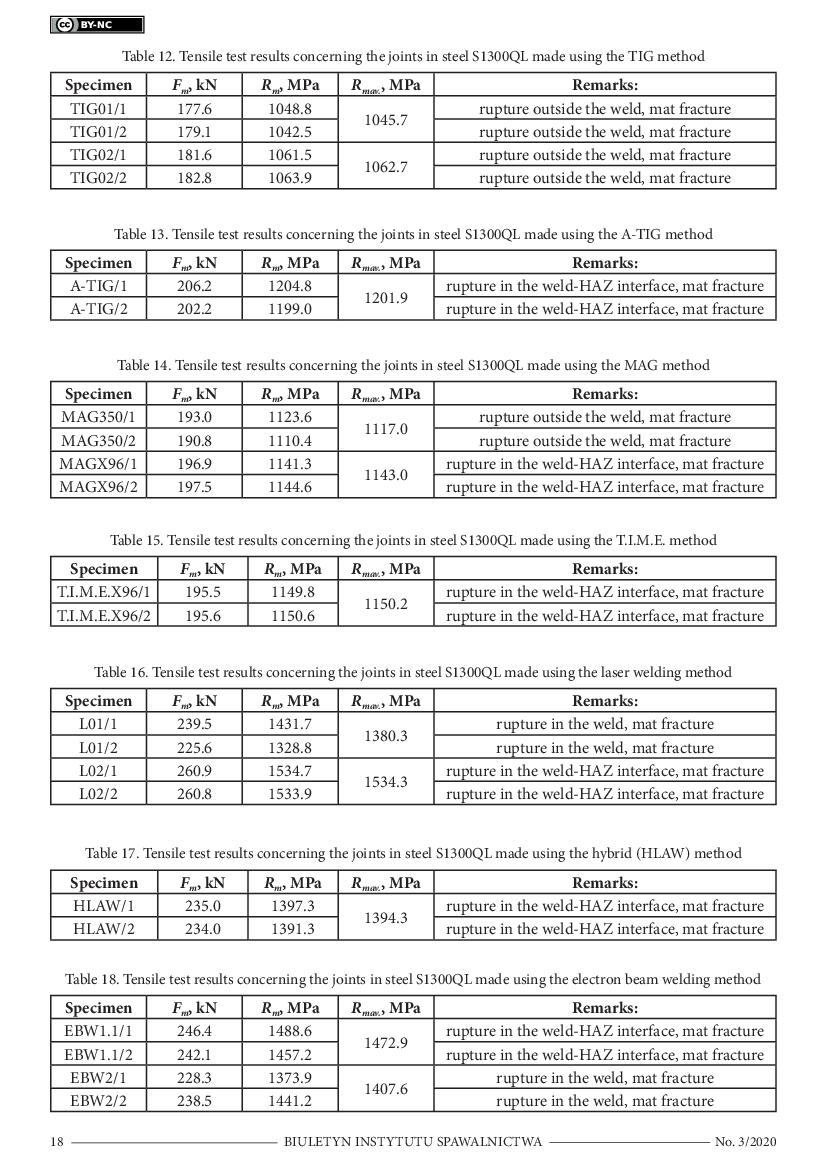
tests. The tests concerning the mechanical properties of the joints with
respect to various welding methods were subjected to comparative analysis. The
research work finished with the formulation of concluding remarks concerning
the mechanical properties of the joints.
doi: 10.17729/ebis.2020.3/1
 1 / 14
1 / 14
 2 & 3 / 14
2 & 3 / 14
 4 & 5 / 14
4 & 5 / 14
 6 & 7 / 14
6 & 7 / 14
 8 & 9 / 14
8 & 9 / 14
 10 & 11 / 14
10 & 11 / 14
 12 & 13 / 14
12 & 13 / 14 14 / 14
14 / 14