The Assessment of the Effect of Technological Conditions of the Laser and Hybrid Welding of Corrosion-Resistant Steels on Welding Fume Emission
Corrosion-resistant steels are used in many industrial sectors, including the food, chemical, petrochemical, power engineering and the building engineering industry. Welding processes constitute the main method enabling the joining of corrosion-resistant steels. Typically, corrosion-resistant steels are joined using manual metal arc welding, gas-shielded metal arc welding (MIG/MAG), flux-cored arc welding, TIG welding and submerged arc welding processes. In turn, advanced welding processes include laser beam, hybrid (laser + arc), plasma arc and electron beam welding methods. The growing popularity of laser methods in enterprises has necessitated the determination of the effect of technological conditions on the emission of welding fume, i.e. the dominant risk factor when welding corrosion-resistant steels. In 2017, welding fume (formed through the condensation and oxidation of metal vapours) was rated among factors of proven carcinogenic effect (in accordance with the requirements of the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC).
 1 / 9
1 / 9
 2 & 3 / 9
2 & 3 / 9
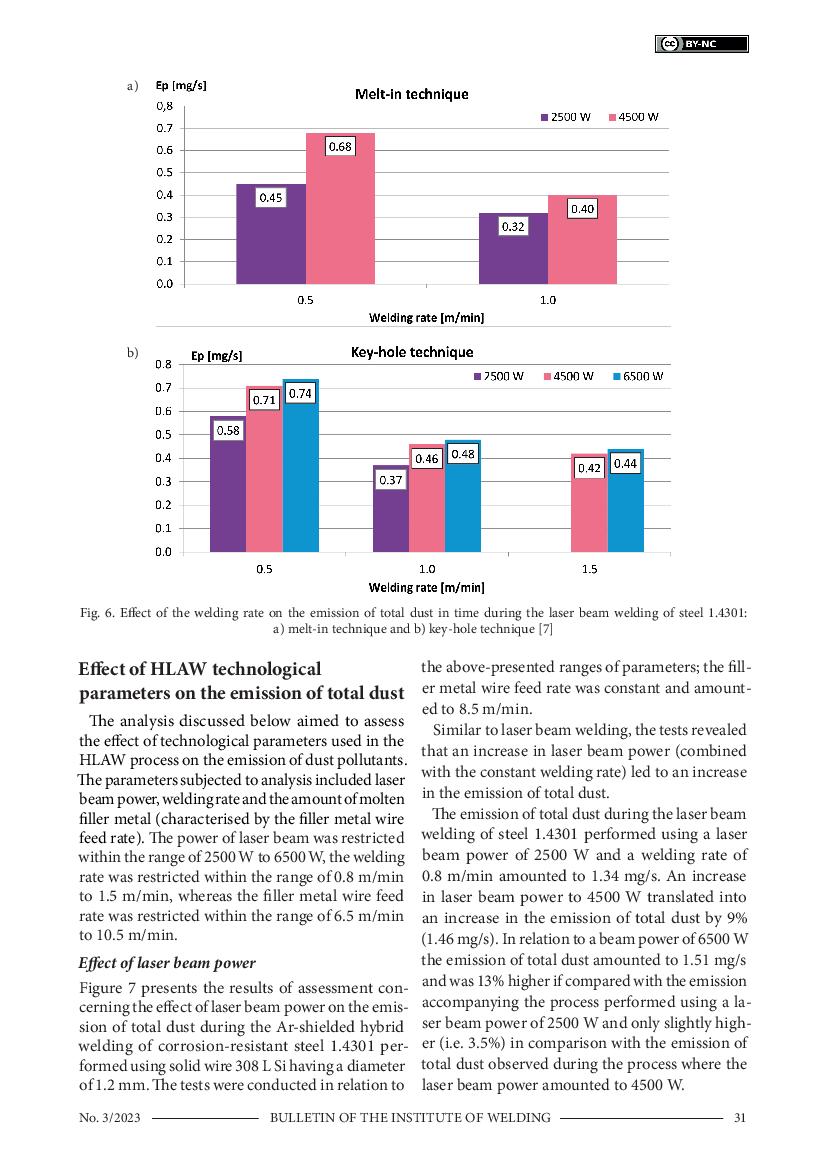
 4 & 5 / 9
4 & 5 / 9
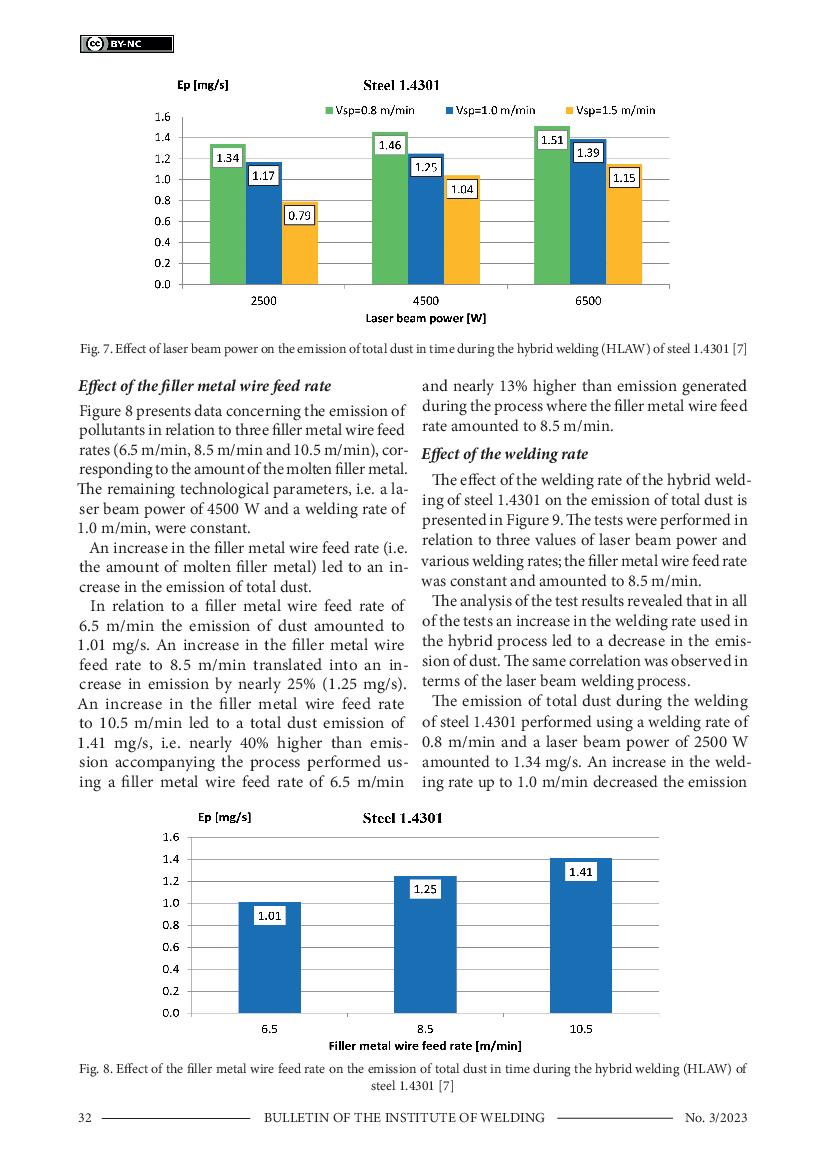
 6 & 7 / 9
6 & 7 / 9
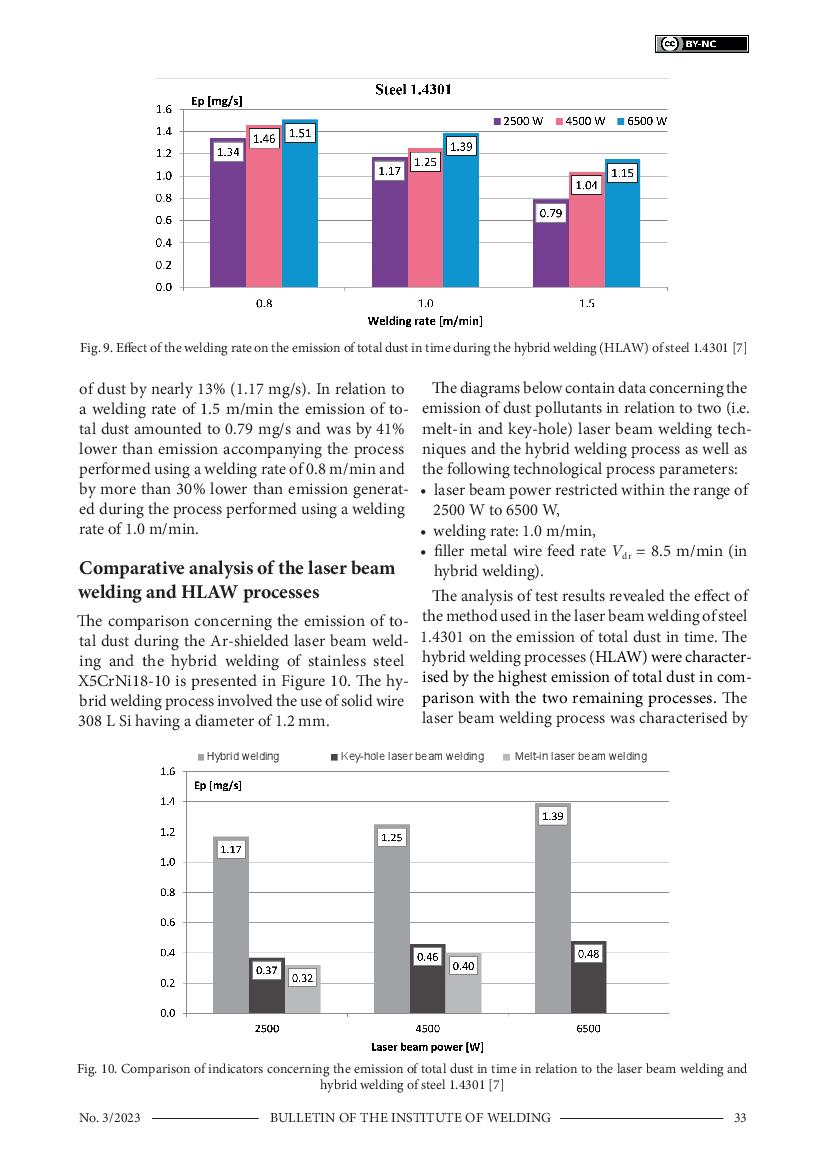
 8 & 9 / 9
8 & 9 / 9