Effect of Nanoparticles on the Structure and Properties of Welds Made of High Strength Low-Alloy Steels
The article presents test results concerning the structure of welds made of high strength low-alloy steel 14HGNDC which, in the molten state, was provided with nanoparticles of various refractory compounds including oxides, carbides and nitrides (TiC, TiN, SiC, VC, NbC, TiO2, Al2O3, MgO and ZrO2). The performed tests revealed the effective use of the nano-oxides of titanium (TiO2) and zirconium (ZrO2) enabling the obtainment of high mechanical properties of the weld metal (Rm -708 MPa and 621 MPa, KCV-20 - 60 J/cm2 and 72,9 J/cm2, a 21 and 19%). The use of a Gleeble 3800 welding cycle simulator made it possible to determine the dependence between temperature ranges of transformations, amount of structural constituents and types of modifying nanoparticles.
 1 / 6
1 / 6
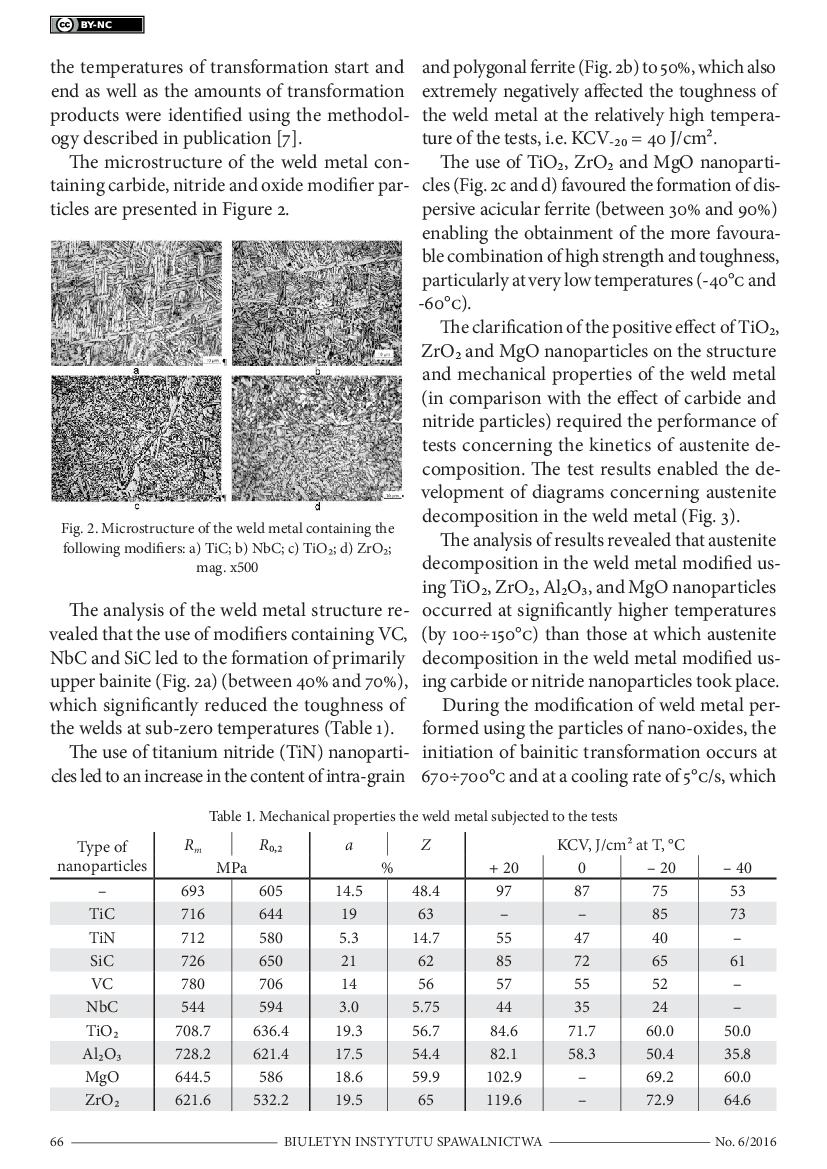
 2 & 3 / 6
2 & 3 / 6
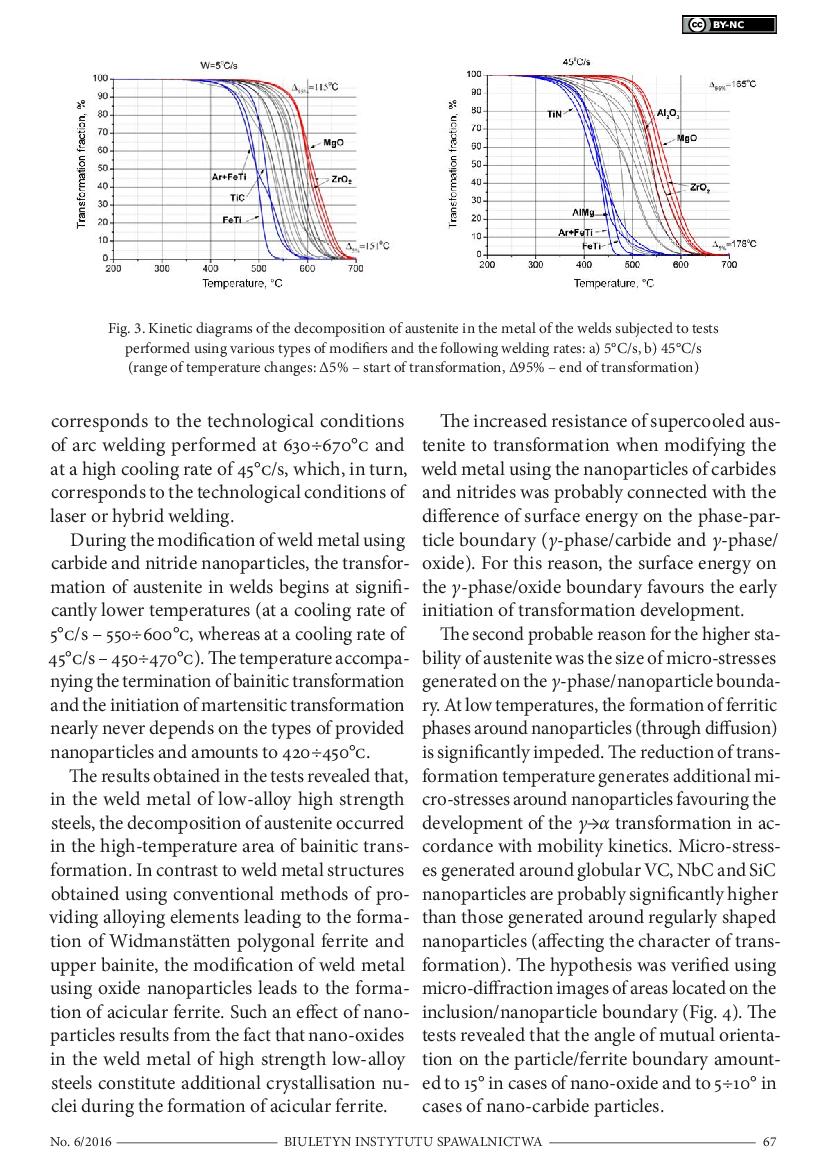
 4 & 5 / 6
4 & 5 / 6 6 / 6
6 / 6