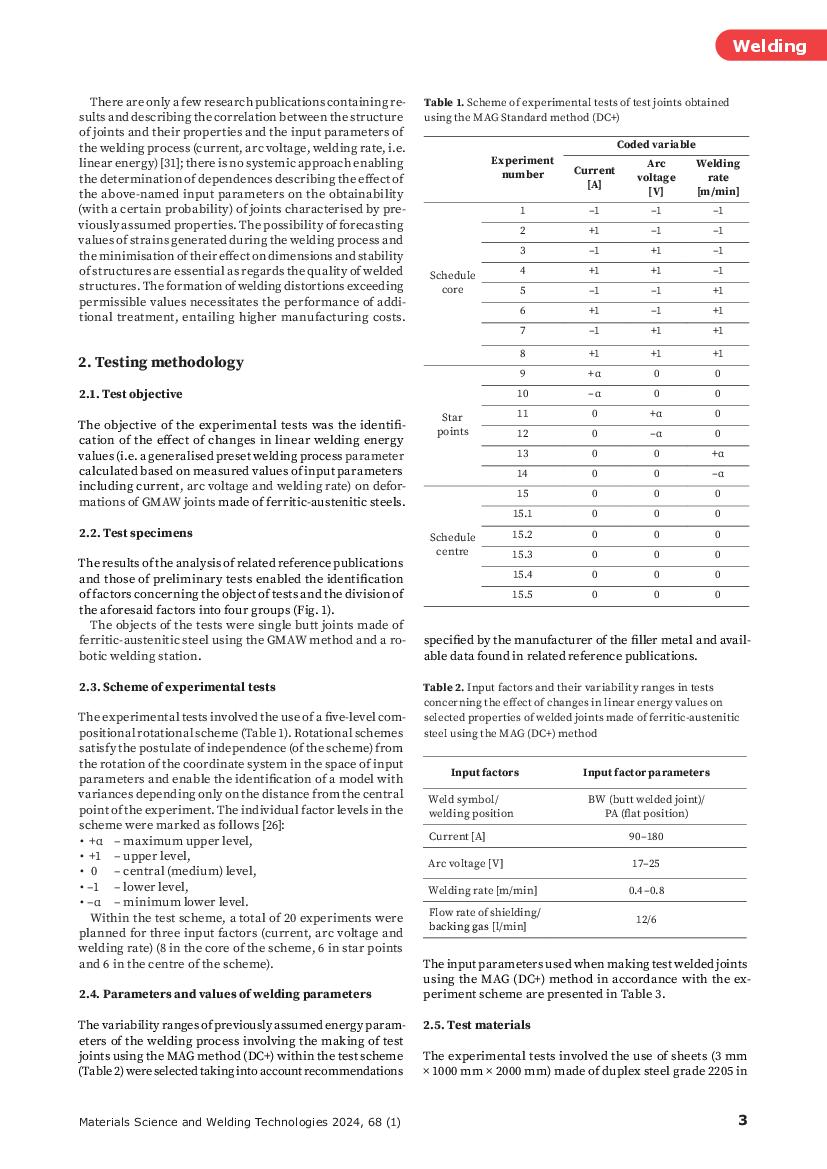
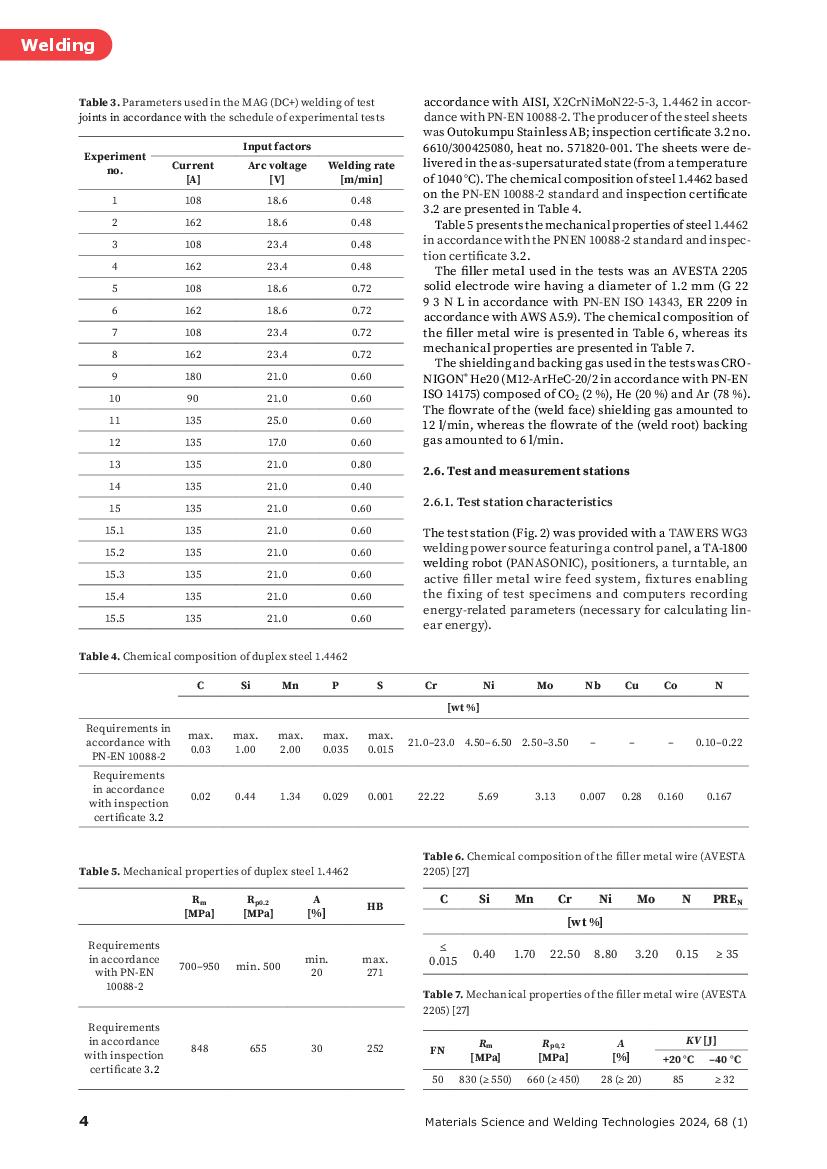
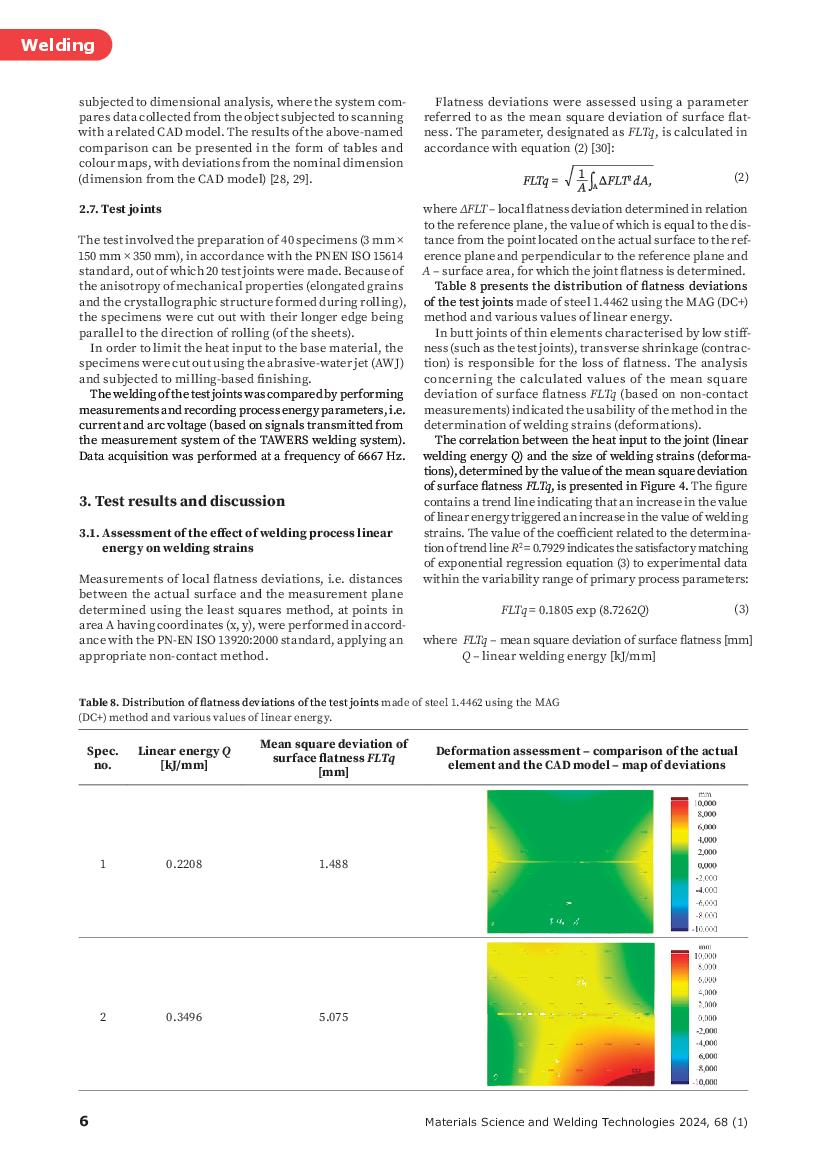
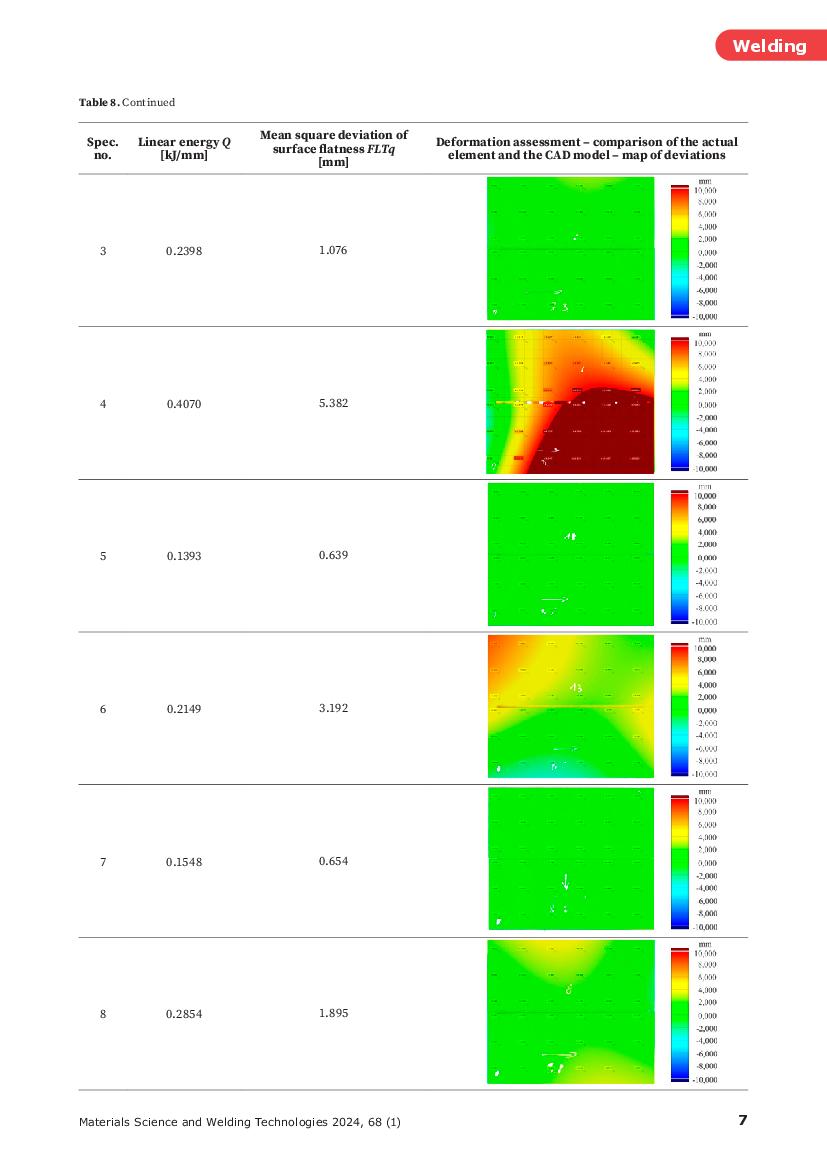
The Effect of a Heat Input to the Joint during the Gas Metal Arc Welding of Ferritic-Austenitic Steel 1.4462 on Welding Deformations
Welding is a special process, the result of which cannot be fully guaranteed despite the use of all possible and available procedures leading to the correct fabrication of the welded joint. The quality of a joint made in the welding process cannot be fully verified during inspection and testing, where any discrepancies may only become apparent during product operation. The aim of the tests presented in the article was to determine the impact of changes in the value of welding linear energy (heat input) and of correlations between values of process parameters (current, arc voltage and welding rate) on welding deformations of joints made of ferritic-austenitic steel using the GMAW method. The testing methodology, involving the performance of tests based on an experimental scheme, enabled the development of a mathematical model of test object (MMTO). The analysis of the MMTO revealed its usability in explaining (and forecasting) the mean square surface flatness deviation (i.e. a parameter used to assess the value of joint flatness deviation) in relation to values of welding process input parameters under specific implementation conditions and assumed significance level α = 0.05. The tests revealed the existence of a narrow range of heat input, in relation to which welding deformations were relatively small (as the correlation between welding deformations and heat input during the welding process was not a monotonic function).
 1 / 12
1 / 12
 2 & 3 / 12
2 & 3 / 12
 4 & 5 / 12
4 & 5 / 12
 6 & 7 / 12
6 & 7 / 12
 8 & 9 / 12
8 & 9 / 12
 10 & 11 / 12
10 & 11 / 12 12 / 12
12 / 12